1.
Define velocity gradient and give its units
2. Define viscosity. How it varies with
temperature
3. Write poiseuillis equation and explain
the terms in i
4. State Bernouli’s theorem for which type
of fluids Bernouli’s theorem is applicable
5. Why canals are constructed in “V”
shape. Explain
Thermal Expansion of materials
7. Can a substance contract on heating. Give an example.
8. Why gap are left between rails on a railway
track.
10. A steel tank is filled with a gas at 150
atmospheres at  . If the pressure rises to 250 atmospheres the tank
explodes. Find the temperature at which the tank explodes.
. If the pressure rises to 250 atmospheres the tank
explodes. Find the temperature at which the tank explodes.
 . If the pressure rises to 250 atmospheres the tank
explodes. Find the temperature at which the tank explodes.
. If the pressure rises to 250 atmospheres the tank
explodes. Find the temperature at which the tank explodes.
Thermo dynamics
11. State Zeroth law of thermodynamics.
12. When will be heat engine having maximum
efficiency.
13. Define efficiency of heat engine
14. What is the specific heat of gas in (a)
isothemal change (b) adiabatic process
15. What are a “Source” and a “Sink” in heat
engine.
Transmission of heat
(VSAQ’S)
16. Define stefan’s law for a black body
17. Give the mathematical expression of
Kirchoff’s law. What is the result.
18. Cooking utensils are coated black
outside, why.
1. Which physical quantity has negative
dimensions of Mass?
2. If the unit of length and force
increased by four times how much increased will be there in unit of pressure?
3. If unit of mass, length and time are
doubled, what happened to unit of energy?
4. What are systematic and random errors?
5. The vertical component of vector is
equal to its horizontal component then what is angle made by the vector with
X-axis?
7. What are unit vector and Null vector? What
is the dot product of ‘i’ and ‘j’?
11. Give an example of a case where the
velocity of an object is zero but its acceleration is not zero.
12. What is the acceleration of a projectile
at the top of its trajectory?
13. Write the two angles of projection for
the same horizontal ranges of a projectile.
14. What is impulse? State its S.I units and
dimensional formula.
15. State the relation between kinetic energy
and momentum.
16. Which physical quantity does the area
between F-S graph represents and S-axis represents?
17. Which physical quantity does the area
between F – t graph represents and t – axis represents?
18. Define co-efficient of restitutions? What
are its practical values.
19. Distinguish between elastic and inelastic
collision.
20. A body freely falling from a certain
height ‘h’ after striking a smooth floor resounds and raises to a height h/4.
What is coefficient of restitution between the floor and body?
21. It is necessary that any mass should be
present at the centre of mass of a system?
22. Can we change the period of oscillation
of swing by sitting and standing on the plank of swing while swinging? Explain?
23. What happens to the frictional force if
the surface is moderately polished and heavily polished?
24. What is normal reaction of the body when
it is at rest on
(a) A horizontal surface
(b) An inclined surface
25. A horse has exert greater force driving
the start of the motion than later. Explain.
26. Why aeroplanes and automobiles are streamlined.
27. A meter scale of mass m is lying
horizontal on the floor of a room. What is the work to be done to make it
vertical.
28. For a stone, what is the ratio of the
distances cohered in its 1st, 3rd, 5th seconds
of its free fall.
29. Define moment of inertia write its unit
and explain its importance.
30. Define torque and radius of gration mention
the factors on which it depends.
31. Give the vector from of relation between
‘r’ and ‘F’
Give the vector from of relation
between ‘L’ and ‘P’
32. Two rigid bodies have same angular
momentum about their axis of rotation which of the bodies will have greater
K.E?
33. Which is the weakest force of all the
basic force in nature?
Which is the strongest force of all
the basic force in nature?
34. Does ‘g’ change with the angular velocity
of rotation of the earth at
(a) the equator and (b) the poles
35. What is a white dwarf and chandrasekhar
limit?
36. Give an example of the principle of equivalence?
37. Hydrogen is in abundance around the sun
and less around the earth explain.
38. What is the time period of revolution of a
geo stationary satellite? Does rotate from west to east or east west?
39. What are the physical quantities having
maximum values at the mean position and the extreme position in SHM?
40. What happens to the energy of “S.H.O” if
its (i) amplitude is doubled?
(ii) Time period is doubled give
relevant equations.
41. The acceleration of a given particle in
SHM is 0.4 ml S2 at a displacement of 0.1m what is the period of
oscillation?
42. A simple harmonic oscillator has a time
period of 2s. What will be the change in the phase after 0.2s after leaving the
mean position?
43. How does the acceleration of a particle
in SHM vary? Where will if be maximum?
How does the velocity of a particle in SHM
vary? Where will if be maximum?
45. State the theoretical and practical
limits of poisson’s ratio?
46. What is elastic fatigue?
47. Define surface tension and give its
dimensional formula.
48. Explain why rain drops are spherical in
nature?
49. Define “angle of contact’ what are its
values for pure water and mercury?
50. What is the effect of temp on surface
tension of wather?
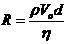







No comments:
Post a Comment